UN-supported initiatives enhanced healthcare, education, and gender equality, focusing on HIV services, STEM, and violence protection


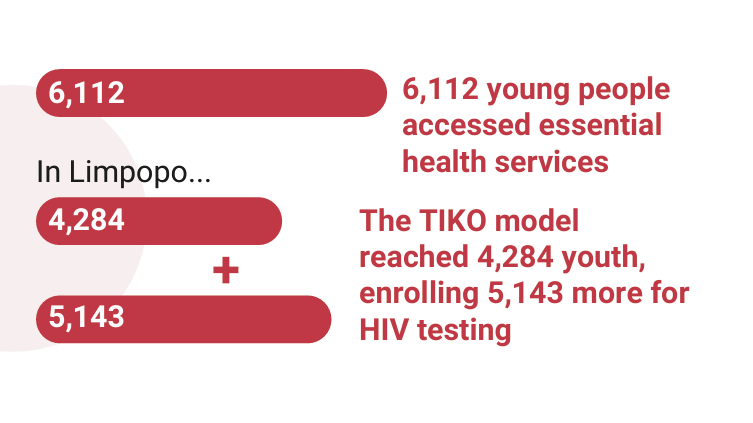
With UN support, 6,112 young people accessed essential services at supported health facilities. In Limpopo, the innovative TIKO model reached 4,284 youth, enrolling 5,143 new participants for HIV testing, contraceptive services, antiretroviral therapy (ART) initiation, and pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP). The initiative significantly increased access to health services and empowered adolescents to take charge of their health. South Africa has the world’s largest paediatric HIV epidemic, with 7,000 new infections among children annually. In response, the UN is driving action and ac countability through the Global Alliance to End AIDS in Children by 2030. Since joining the initiative, 12,000 children have initiated treatment.
To strengthen youth access to quality healthcare, the Safeguard Young People Programme upgraded 91 health facilities across KwaZulu-Natal, Eastern Cape, and Limpopo. Through improved data systems and provider training on rights-based, integrated sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR), HIV, and gender-based violence (GBV) services, the initiative is advancing youth-friendly, comprehensive care that empowers young people to take charge of their health. At the national level, the UN supported the finalization of the Global HIV Prevention Roadmap in collaboration with the National AIDS Council and addressed adolescent pregnancy in Limpopo through a Critical Thinking Forum.

South Africa has made notable strides in building resilient and inclusive health systems, with strong backing from the UN, particularly in advancing the implementation of the National Health Insurance (NHI) Act as a step toward Universal Health Cover age (UHC). UN contributions have also been pivotal in shaping national health policies grounded in hu man rights, encompassing sexual and reproductive health, as well as both communicable and non-communicable diseases.
Notable progress in non-communicable disease (NCD) management includes the development of national guidelines for cardiovascular disease and a policy on drug and alcohol dependence treatment. These advancements reflect strong policy frameworks, evidence-based decision-making, and growing multisectoral and community engagement in health governance.
To combat teenage pregnancy, the UN released a powerful policy brief analysing District Health Information System (DHIS) data to identify hotspot areas, sparking urgent dialogue at a high-level critical thinking forum with government and multi-sector partners. The forum’s key outcomes— highlighting the alarming rise in pregnancies among 10 to 14-year-olds and the urgent need for research into the lived experiences of teenage mothers—were featured in a widely circulated news article.
To meet the growing demand for health services in supported districts, peer educators were equipped through a cascading model in comprehensive sexuality education (CSE) for out-of-school youth. In 2024, a national workshop with curriculum officials and special needs educators critically reviewed the Breaking the Silence manual, resulting in a clear roadmap for updating lesson plans, strengthening master trainer capacity, and improving the alignment and application of teaching materials.
The UN’s national survey on condom accessibility revealed critical last-mile distribution gaps, with most supplies limited to government facilities and failing to adequately serve the LGBTQI+ community. To address this, the Safeguard Young People programme launched an innovative partnership with the KZN Taxi Association, training drivers and distributing over 182,000 condoms alongside targeted educational materials to reach commuters with safer sex messaging.


Through UN-supported, district-led interventions, the number of zero-dose children was reduced by 43% in three targeted districts within six months. This was achieved by strengthening local planning, community profiling, capacity-building of community health workers, and enhancing monitoring and evaluation systems.
To reinforce national immunization efforts, training materials and guidelines on vaccine management were distributed to 3,000 primary healthcare facilities. In parallel, 308 managers and clinicians were trained on child wasting indicators, caseload estimation, and nutrition supply forecasting. The nation al Global Alliance dashboard was also developed and institutionalized, improving real-time monitoring and response capacity.

The UN’s WASH emergency response directly benefited over 17,000 individuals and learners, improving access to essential water, sanitation, and hygiene services. Through social media and community radio, more than 4 million caregivers received vital information on health, nutrition, and sexual and re productive health. At the same time, youth-led environmental initiatives engaged 60 schools and 7 universities, fostering long-term community-driven change.

Responding to cholera and Mpox outbreaks, the UN deployed a multimedia truck, reaching over 200 individuals in high-risk communities with critical health information. Complementing this, digital platforms such as U-Report were used to expand outreach and conduct a rapid qualitative assessment to inform Mpox vaccine strategies.


In close partnership with South Africa’s Department of Health, the United Nations has contributed significantly to the transformation of national food systems, promoting equitable livelihoods, sustainable production, and better nutrition for children. This collaboration led to the development of food labelling and marketing regulations, enhanced nutrition management capacity, and the integration of critical malnutrition indicators into the national health system. Moreover, 1.8 million youth were mobilized to advocate for healthier school food environments, aligning policy and practice to combat obesity and promote improved nutrition outcomes.



The UN supported the completion of Learning and Teaching Support Materials (LTSM) for children aged 0–4 years, addressing key challenges in early childhood education. Under the Foundation Phase Initiative (FPI), over 16,000 educators and 10,700 school leaders were trained, enhancing learning for approximately 652,000 children.
The P.L.A.Y. online platform continued to deliver impactful in-service teacher training, with 148,624 new users registered in 2024 and a 50.1% course completion rate, exceeding global benchmarks. As a result, an estimated 1.86 million children benefited from improved teaching practices.

Enhancing literacy, numeracy, and digital learning through the Early Grade Reading Programme (EGRP), the UN advanced literacy and numeracy outcomes. In the Northern Cape, 635 teachers were trained, reaching 21,945 learners; in the North West Province, 735 teachers supported 25,400 learners. As part of the GIGA global initiative, the UN facilitated improved school connectivity and digital learning by mapping all schools—except in the Western Cape—to support ICT planning. The Siyavula and Junior Tukkies online platforms expanded access to math and science education, reaching over 1.5 million and 654,000 learners, respectively.

A major milestone in 2024 was the approval of the National Coding & Robotics Curriculum by Umalusi. The UN supported the Department of Basic Education in training 1,032 teachers (59% female), benefiting 62,515 learners (54% girls) across 1,011 schools. To address resource gaps in low-quintile schools, the UN provided 150 LEGO Spike Prime Kits, 125 laptops, and other essential equipment to five provinces. These contributions supported the creation of Coding & Robotics hubs that will serve as training centers for surrounding schools, expanding access to quality STEM education in underserved communities

Story of Change: Girls in STEM: Coding and robotics are the future

“My name is Ayanda Mkhulisi, and I’m currently in Grade 11 at Mt Curry Senior Secondary School. When coding and robotics were introduced to us, I felt excited and curious, because robotics is the future. Many industries already use robots in production, and I believe that, in time, they will play a major role across sectors. I always wanted to become an accountant, but learning about coding and robotics changed my perspective. Although it’s a field still dominated by men, I’m not afraid to step into it as a young woman. I want to make a difference in my community. I’m deeply grateful to UNICEF for training our teachers to become champions in this subject.”
Seventeen-year-old Ayanda lives in a rural area near the town of Kokstad with her aunt, her legal guardian, and three cousins. She lost both parents—her father in 2011 and her mother in 2012—and has no siblings. Despite limited school resources, including a short age of computers and poor internet connectivity in the area, Ayanda remains determined to pursue her dreams.



The UN has made significant progress in advancing policy reforms to address gender-based violence (GBV). In February 2024, a high-level consultation convened 40 delegates to finalize a Discussion Pa per on Non-Custodial Measures for Adult Offenders, focusing on alternative sentencing approaches in GBV cases.
As part of efforts to enhance national systems for preventing and responding to GBV, 395 professionals received training in forensic evidence management and DNA handling, bolstering both investigative and judicial capacities.
The UN also provided technical support for key regional and global frameworks, including Beijing +30, CSW Resolution 60/2, and the SADC Strategy for Addressing GBV. A high-level, three-day regional meeting brought together stakeholders to assess progress, identify gaps, and plan the next steps on GBV, HIV/AIDS, and gender inequality. Outcomes included the evaluation of CSW 60/2 implementation, the adoption of a regional monitoring and evaluation (M&E) framework, and preparations for CSW69 and Beijing +30.
At the community level, four educational workshops engaged 190 traditional and religious leaders across the eThekwini, Ugu, and uThukela districts. Using clinical data to emphasize sexual and reproductive health rights (SRHR), gender justice, and women’s empowerment, the workshops supported leaders in developing actionable plans to combat GBV in their communities.
In the Western Cape, gender-sensitive training was delivered at 40 police stations, leading to the re vision of police case forms to better support the LGBTQI+ community and promote a more intersectional approach to justice. Additionally, HeForShe dialogues were expanded to 15 sites in KwaZulu-Natal, engaging men and boys in challenging harmful gender norms and promoting accountability among local leaders.

Through the Global Fund AYP Programme and PEP FAR, the UN empowered 11,768 education stake holders, including school management teams, governing bodies, and parents, to promote com prehensive sexuality education (CSE) and combat school-related violence. This initiative contributed to safer, more inclusive school environments.
Further efforts included partnerships with the government on the “Let’s Talk EUP” dialogues and the 16 Days of Activism campaign, led by education officials to address GBV, early pregnancies, and violence in schools. These initiatives reached 1,456 young people, promoting awareness and action at the community level.
In addition, 776 officials across multiple provinces participated in Parent-Child Communication workshops, equipping them with the tools to foster healthier relationships and improved learning environments for students and educators.

